
Screw pump is a part of the dry compressed gas transfer pump series. They are positive displacement pumps that use one or more screws to move fluid or water along the screw shaft. These screws interlock to pressurize the fluid and move it into the system. These screws engage each other and reciprocate in the cavity of the cylinder. They are often used in industrial vacuum applications, often in combination with Roots blowers, and as oil-free roughing pumps in high vacuum and ultra-high vacuum systems.
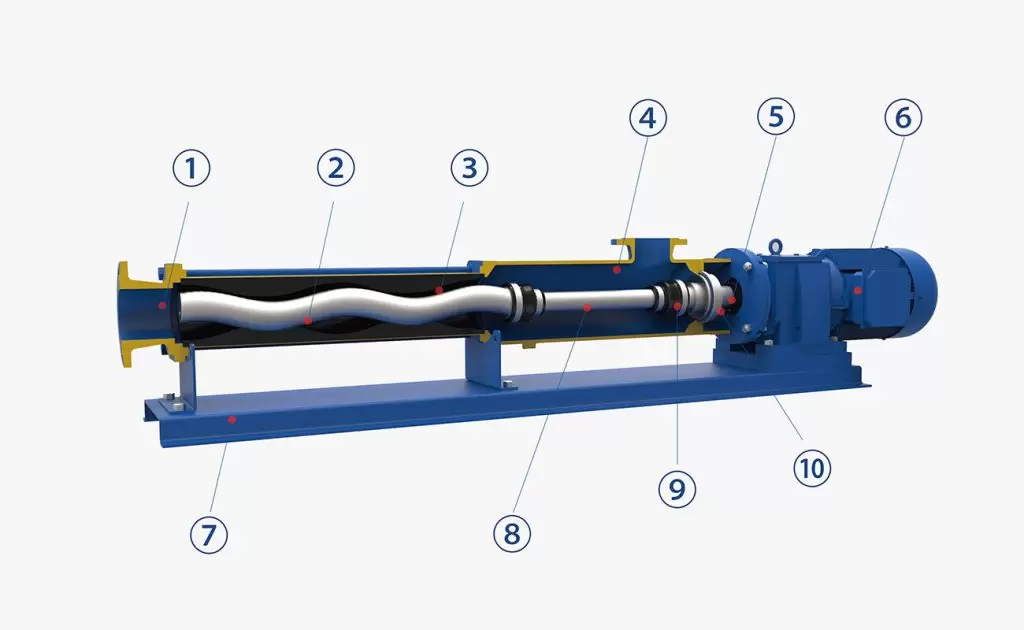

The Rotor of a Progressive Cavity Pump
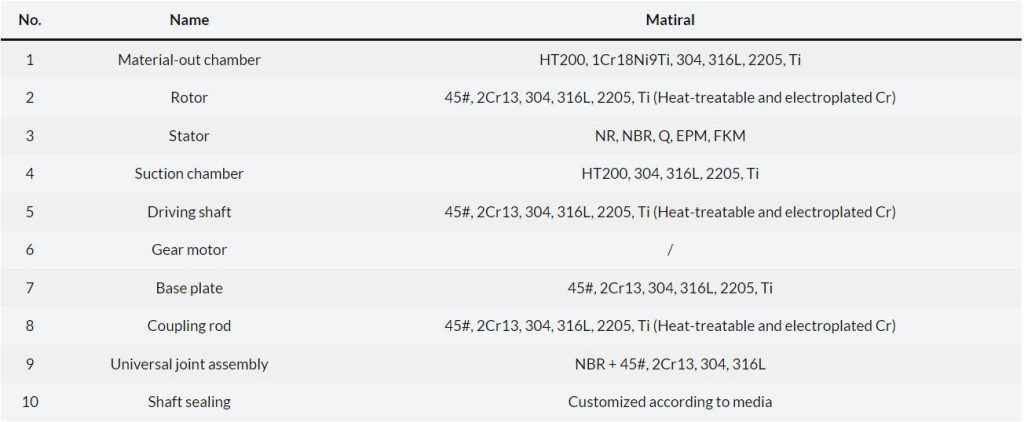
The Progressive cavity pump rotor (also known as the main shaft) is mostly made of stainless steel, and can be selectively plated with chrome;
Due to its meshing relationship with the characteristic geometry of the stator, in addition to natural wear, it is also whether the conveyed medium contains solid particles and corrosive.
The rotor is an essential component of a screw pump. It is a cylindrical or conical-shaped shaft with a helical screw thread wrapped around it. When the rotor rotates inside the stator, the screw thread forms a series of chambers that trap and move the fluid from the pump inlet to the outlet.
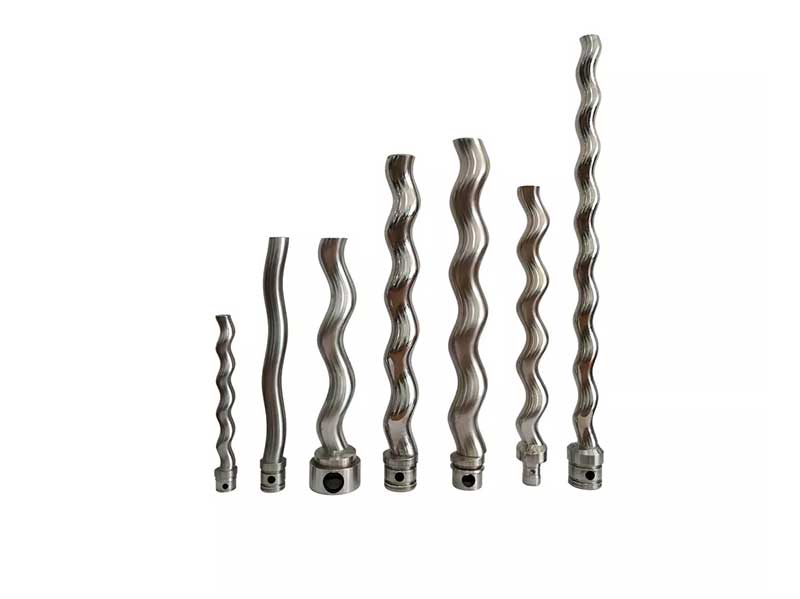
The geometry of the rotor screw thread can vary depending on the type of screw pump. In general, there are two types of rotors used in screw pumps: single screw and twin screw. Single screw rotors have a single helical thread, while twin screw rotors have two intermeshing helical threads.
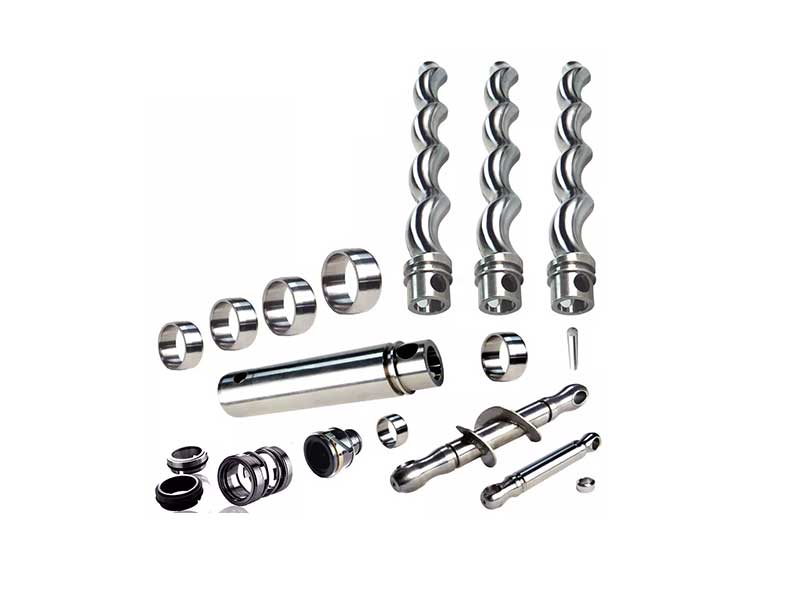


The material used for the rotor is also critical to the pump’s performance and longevity. Rotor materials should have high wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. Common materials used for rotor construction include stainless steel, bronze, and various alloys.
One of the critical factors that affect the pump’s performance is the clearance between the rotor and the stator. The rotor’s helical screw thread should be closely matched to the stator’s internal profile to ensure that there is minimum clearance between the two components. This ensures that the fluid is effectively trapped and moved along the screw thread without any leakage.

The rotor’s rotational speed also plays a critical role in the pump’s performance. A higher rotational speed leads to increased flow rate and pressure, but it also increases wear and tear on the rotor and stator. Therefore, the rotor speed should be optimized to balance performance and longevity.
In conclusion, the rotor is a critical component of a screw pump. Its design, material, and clearance affect the pump’s performance and longevity. Proper maintenance and care of the rotor can ensure optimal pump performance and longevity.

Here are some common questions and answers about screw pump rotors:
Q: What is a screw pump rotor?
A: A screw pump rotor is a component of a screw pump that rotates inside the stator, creating a cavity that moves fluid from the pump’s suction to discharge side.
Q: What materials are screw pump rotors typically made of?
A: Screw pump rotors are commonly made from materials such as stainless steel, hardened steel, and elastomers. The specific material used depends on the application requirements and the fluid being pumped.
Q: What are the different types of screw pump rotors?
A: The two most common types of screw pump rotors are single-head and double-head rotors. Single-head rotors have a single helix, while double-head rotors have two helices that run in opposite directions.
Q: What are some advantages of using a screw pump rotor?
A: Screw pump rotors offer several advantages, including the ability to handle fluids with varying viscosities, low pulsation flow, and high volumetric efficiency. They are also capable of handling abrasive and corrosive fluids.
Q: How do I select the right screw pump rotor for my application?
A: To select the right screw pump rotor, you should consider factors such as the type of fluid being pumped, the pump’s flow rate and pressure requirements, and the temperature and viscosity of the fluid. Consulting with a pump specialist can also be helpful in selecting the appropriate rotor.
Q: How do I maintain and replace a screw pump rotor?
A: Regular maintenance is essential for prolonging the life of a screw pump rotor. This includes cleaning the rotor and stator, inspecting for wear and damage, and replacing worn or damaged components. Replacement rotors can be purchased from the pump manufacturer or a third-party supplier.
Q: Are there any common problems with screw pump rotors?
A: Common problems with screw pump rotors include wear, corrosion, and damage from abrasive fluids. Regular maintenance and proper material selection can help minimize these issues.
In conclusion, screw pump rotors are critical components of screw pumps and offer several advantages for pumping fluids in various industries. Proper material selection, regular maintenance, and replacement when necessary can help ensure efficient and reliable pump operation.

